
For reasons of economics and convenience, industrialized societies today rely primarily on oil (petroleum) and natural gas for their energy needs. Oil and natural gas consist of hydrocarbons, chainlike or ring-like molecules made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. For example, bottled gas (propane) has the chemical formula C3H9. Chemists consider hydrocarbons to be a type of organic chemical, so named because similar chemicals make up living organisms.
Some hydrocarbons are gaseous and invisible, some resemble watery liquids, some appear syrupy, and some are solid (Fig. 2). The viscosity (ability to flow) and the volatility (ability to evaporate) of a hydrocarbon product depend on the size of its molecules. Hydrocarbon products composed of short chains of molecules tend to be less viscous (they can flow more easily) and more volatile (they evaporate more easily) than products composed of long chains, simply because the long chains tend to tangle up with each other. Thus, short-chain molecules occur in gaseous form at room temperature, moderate-length-chain molecules occur in liquid form, and long-chain molecules occur in solid form as tar.
Why can we use hydrocarbons as fuel? Simply because hydrocarbons, like wood, burn—they react with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water, and heat. As an example, we can describe the burning of gasoline by the reaction
2C8H18 + 25O2→16CO2 + 18H2O + heat energy
During such reactions, the potential energy stored in the chemical bonds of the hydrocarbon molecules converts into usable heat energy.
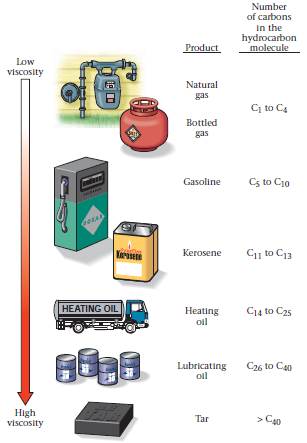
FIGURE 2. The diversity of hydrocarbon products we use: natural gas piped to houses for heating and cooking, bottled gas (propane), gasoline for cars, kerosene for heating or illumination, diesel fuel for trucks, lubricating oil for motors, and solid tar, which melts when heated and can be used to make asphalt. Note that these products are listed in order of increasing viscosity.
Дата добавления: 2015-09-12; просмотров: 16 | Поможем написать вашу работу | Нарушение авторских прав |