
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative | |||||||||
| I You He She It We You They | have
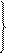 has
have
has
have
| worked | I You He She It We You They | have not
 has not
have not
has not
have not
| worked | Have
Has
Have | I you he she it we you they | worked? | |||
The Present Perfect is formed with the auxiliary to have in the Present Indefinite + the Past Participle: I have just finished my work.
The Past Participle in regular verbs has exactly the same form as the Past Indefinite: lov ed, walk ed, etc.
The negative is formed by adding not to the auxiliary to have in the Present Indefinite + the Past Participle.
The interrogative is formed by inverting the auxiliary to have in the Present Indefinite and the subject+ the Past Participle.
USAGE
The Present Perfect is used to denote:
1 ) a completed action connected with the present. Attention is centred on the action itself or on the result of the action: I' ve changed everything.
2) an action completed before a definite moment in the future in adverbial clauses of time after the conjunctions when, till, until, before, after, as soon as: I am not going till you have answered me
3) an action which began in the past, has been going on up to the present and is still going on. The preposition for is used to denote the whole period of duration. Since is used to indicate the starting point of the action. If the conjunction since introduces a clause, the verb in this clause is in the Past Indefinite: Where have you been since last Thursday?
4) opening up a conversation, introducing a new topic or summing up a situation: I'm afraid I' ve been terribly boring and talked too much.
5) a recent action when the time is not mentioned: I have read the rule but I don`t understand it.
6) an action which is over, but the period of time within it was performed is not yet over at the moment of speaking (with the words today, this week, this year, etc): I have seen her today.
Such phrases as It's the first/second/etc time... are followed by the present perfect
Eg. It's the second time I've been on a plane.
 The following words and time expressions can be used with the Present Perfect:
The following words and time expressions can be used with the Present Perfect:
today/ this week/ month / year, etc. denoting an incomplete period of time: Have you seen him today? (= at any time today).
just, lately, recently, yet (in negative sentences and in interrogative sentences when it corresponds to the Russian word "уже"), already (in affirmative sentences; and in interrogative sentences to express surprise), ever, never, before, and in some cases always.
Дата добавления: 2015-09-12; просмотров: 20 | Поможем написать вашу работу | Нарушение авторских прав |