
Читайте также:
|
1. An integral (total) flow of the solar radiation is measured by pyranometer (e.g. Yanishevskiy’s pyranometer). The measure units are 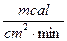 . The solar constant is 2
. The solar constant is 2 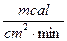 at the upper atmosphere and 1
at the upper atmosphere and 1 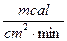 near the earth surface.
near the earth surface.
2. Biological method – an erythemal dose determination using the Gorbachov’s biodosimeter (fig. 2.2). A minimal erythemal dose (MED) or biodose is the shortest exposure time to the UVR (minutes), which causes the barely perceptible reddening (erythema) on non-tanned skin 15-20 hours after the exposure (for children - 1-3 hours).
Gorbachov’s biodosimeter is 6-window (1.5×1.0 сm) plane-table with the sliding cover, that may close all or some of the windows. This device (biodosimeter) is fixed on the non-tanned skin (the internal surface of the forearm) to determine the biodose. It is useful to mark the window numbers and locations on the skin. After warming up of the lamp (10-15 minutes), a student is exposed to an artificial source of the UVR at the distance of 0.5 m. Then the window #1 is opened, and after that we open a new window every minute. This way, the window #1 is irradiated for 6 minutes, #2 – 5 minutes, #3 – 4 minutes, #4 – 3 minutes, #5 – 2 minutes, #6 – 1 minute. The exposure time and distance may be different depending on a power of the UVR source and other conditions.
The skin is checked for the reddening 18-20 hours after. An erythemal dose is the exposure time of a window with the smallest erythema.
A physiological dose is 1/2 - 1/4, and a preventive dose is 1/8 of erythemal dose.
A preventive dose for the exposure distance, required for the patient can be calculated using the following formula:

where В is a distance from the lamp to the patient in meters;
С – a standard distance for the determination of a preventive dose in meters, (0.5 m);
А – an erythemal dose at a standard exposure distance in minutes.
Comment: As it’s above mentioned, students will only perform the first phase of the biological method measuring during this lesson. They will irradiate the forearm skin of each other using the Gorbachov’s biodosimeter and indicate numbers of windows on the skin. Students will be able to determine the erythemal dose after 18-20 hours. Then they should write it down in the protocol and prepare the calculations of the physiological and preventive doses for themselves for the next lesson.

Fig. 2.2. Gorbachov’s biodosimeter.
3. Photochemical (Oxalic Acid) method was elaborated by Z.N. Kylichkova. It is based on the oxalic acid decomposition being in proportion with the intensity and duration of the UV irradiation in the presence of nitrate uranil.
Measuring result is the mass (in milligrams) of the decomposed oxalic acid per 1 cm2 of the solution surface. An erythemal dose is 3.7 – 4.1 mg/cm2 of the decomposed oxalic acid, a physiological dose is 1 mg/cm2, a preventive dose is 0.5 mg/cm2.
Intensity of the ultraviolet radiation can be determined using this method as the mass (in milligrams) of the decomposed oxalic acid per 1 cm2 of the solution surface per certain amount of time (day, hour).
Reagents: 0.1 n. oxalic acid solution (6.3 g per liter of distilled water); effecting 0.1 n. solution of potassium permanganate (3.16 g КМnО4 per liter of distilled water): effecting 0,1 n. solution of the oxalic acid and nitrate uranil (6.3 g of oxalic acid and 5.02 g of nitrate uranil per liter of distilled water); 6 % solution of sulphuric acid (60 ml of concentrated acid per liter of distilled water).
Order of testing:
1. The titer of 0,1 n. solution of potassium permanganate КМnО4 by 0.1 n. solution of the oxalid acid (Т) has to be determined. For this the following should be done: 25 ml of H2SO4 and 25 ml of 0.1 н. solution of the oxalic acid are poured into the volumetric flask, then it is warmed up to 700C on a bain-marie, and titrated by 0.1 n. solution of KМnО4 from a burette until the appearance of the minimally perceptible pink color, that remains visible for 1 minute. The titer is calculated by dividing the volume of the oxalic acid by the volume of the KМnО4 solution, used in the procedure.
2. An initial volume of КМnО4 solution on effecting solution of oxalic acid with uranil (V1), which will be exposed to the UVR is determined. For this, the solution of pure oxalic acid is replaced by 25 ml of the effecting solution of oxalic acid with nitrate uranil. The titration process is similar.
3. This solution is exposed in a desired place to determine the UVR intensity there. 25 ml of the effecting solution of oxalic acid with nitrate uranil is poured into a quartz test-tube. This test-tube is overshadowed by black paper with light-window of a certain size.
A closed test-tube is exposed to the sun for a day (to determine the intensity of the Sun or the sky UVR) or to an artificial source of the UVR for an hour (LE-30 lamp, MQ etc). The test-tube is kept in a light-tight case after this exposure.
Comment: Student are provided with pre-made solution to speed up the work.
4. The volume of КМnО4 solution by solution of oxalic acid with nitrate uranil after an exposure (V2) is determined similarly. The difference between an initial volume of КМnО4 solution and a volume of oxalic acid solution after an exposure to the UVR is the volume of decomposed oxalic acid.
Intensity of the UVR is determined as the mass (in mg) of the decomposed oxalic acid per 1 cm2 of the surface of solution during the exposure time (hour).
Intensity of the UVR may be calculated by this formula:
Х =  ,
,
where:
Т – a titer 0.1 n. solution of КМnО4 determined by oxalic acid;
V1 and V2 – volumes of КМnО4, used for titration of oxalic acid with nitrate uranil, before and after an exposure of the UVR, in ml;
6.3 (mg) – the mass of oxalic acid per 1 ml of 0.1 n. solution;
S – a light-window area of quartz test-tube, cm2;
t– the time of a test-tube exposure to the source of the UVR, in hours (to the sun) or minutes (to the artificial source of the UVR).
Comment. The result of the UVR measuring is determined as a mass (in mg) of decomposed oxalic acid per 1 cm2 per minute (from artificial source) or per hour (from the sun).
Conclusion (example). The intensity of the solar UVR, determined by this method is 1.3  of decomposed oxalic acid. This is 0.3 of an erythemal dose. A man needs to receive at least 1/8 of an erythemal dose every day, for this he is required to spend 24 minutes each day outdoors.
of decomposed oxalic acid. This is 0.3 of an erythemal dose. A man needs to receive at least 1/8 of an erythemal dose every day, for this he is required to spend 24 minutes each day outdoors.
4. Physical (photoelectrical) method measures the intensity of the UVR with the ultravioletmeter (short form is uphymeter). Uphymeter is a device containing the magnium (for length range of 220-290 nm) or stibium-caesium (290-340 nm) photoelement. Results of the measuring are represented in mW/cm2 or mcW/cm2.
Due to the erythemal effect being different at various wave length, and being maximal one when l=297 nm, a special unit – microer is introduced. 1 mcer =1 mcW/cm2 when l= 297 nm. The results in mcW/cm2 have to be multiplied by the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) (tabl.1) if the wave length is different.
E.g., the intensity of the UVR, measured by an uphymeter, is 6 mcW/cm2, of which 4 mcW/cm2 at l=297 nm, and 2 mcW/sm2 at l=310 nm. Radiation dose is: 4´1+2´0,03=4,06 mcer. It has been determined, that 1 MЕD=700-1000 mcer; and 1 preventive dose – 100 mcer.
Table 1
Дата добавления: 2015-09-11; просмотров: 144 | Поможем написать вашу работу | Нарушение авторских прав |