
Читайте также:
|
The nuclear explosion occurs. How does the radius of the fireball depend on the time? (Sedov's problem)
Pulling Strings (MIT)
A mass m is attached to the end of a string. The mass moves on a frictionless table, and the string passes through a hole in the table (see Figure P.1.9), under which someone is pulling on the string to make it taut at all times. Initially, the mass moves in a circle, with kinetic energy  . The string is then slowly pulled, until the radius of the circle is halved. How much work was done?
. The string is then slowly pulled, until the radius of the circle is halved. How much work was done?

Collision of Mass–Spring System (MIT)
A mass  with initial velocity
with initial velocity  strikes a mass-spring system
strikes a mass-spring system  initially at rest but able to recoil. The spring is massless with spring constant k (see Figure P. 1.22). There is no friction.
initially at rest but able to recoil. The spring is massless with spring constant k (see Figure P. 1.22). There is no friction.
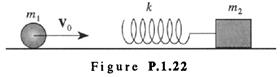
a) What is the maximum compression of the spring?
b) If, long after the collision, both objects travel in the same direction, what are the final velocities 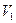 and
and  of
of  and
and  respectively?
respectively?
Relativistic Rocket (Rutgers)
A rocket having initially a total mass  ejects its fuel with constant velocity
ejects its fuel with constant velocity 
 relative to its instantaneous rest frame. According to Newtonian mechanics, its velocity V, relative to the inertial frame in which it was originally at rest, is related to its mass M(V) by the formula
relative to its instantaneous rest frame. According to Newtonian mechanics, its velocity V, relative to the inertial frame in which it was originally at rest, is related to its mass M(V) by the formula

a) Derive this result.
b) Suppose the velocity of the ejecta is limited only by  and derive the relativistic analogue of the above equation. Show that it reduces to the Newtonian result at the appropriate limit.
and derive the relativistic analogue of the above equation. Show that it reduces to the Newtonian result at the appropriate limit.
Compton Scattering (Stony Brook, Michigan State)
In the Compton Effect, a γ - ray photon of wavelength λ strikes a free, but initially stationary, electron of mass m. The photon is scattered an angle θ and its scattered wavelength is  . The electron recoils at an angle φ (see Figure P.2.10).
. The electron recoils at an angle φ (see Figure P.2.10).

a) Write the relativistic equations for momentum and energy conservation.
b) Find an expression for the change  in the photon wavelength for the special case
in the photon wavelength for the special case  .
.
Particle Creation (MIT)
Consider a photon of energy  incident on a stationary proton. For sufficiently large
incident on a stationary proton. For sufficiently large  a π meson can be produced in a reaction
a π meson can be produced in a reaction

What is the  threshold photon energy for this reaction to occur?
threshold photon energy for this reaction to occur?
Дата добавления: 2015-09-11; просмотров: 82 | Поможем написать вашу работу | Нарушение авторских прав |
| <== предыдущая лекция | | | следующая лекция ==> |
| Symmetry. | | | Choose the correct alternative. |