
|
Читайте также: |
To track down useful minerals or other substances below the ground the geologist gathers all information already known about the area to be explored. Next, he or she maps this geologically, noting surface clues like faults and gangue minerals including quartz. Then the geologist can bring to bear any of a battery of tests. Geochemical tests analyze rock and other samples for trace elements that may lead the geologist to a major ore body. Geophysical tests include the following. Geiger counters or scintillation counters detect radioactive substances such as uranium. Gravimeters reveal variations in the density and identify the composition of underlying rocks.
|
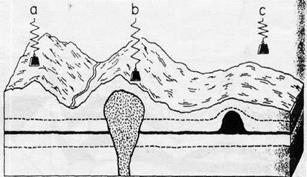
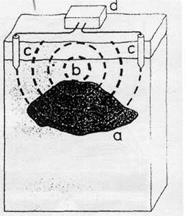
Magnetometers indicate buried iron ores. Because iron is often found with sulfides, magnetometers may lead indirectly to non-ferrous metals, too.
|
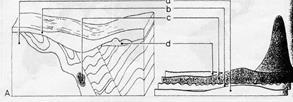
Electrical surveys show certain ores affecting natural ground currents related to the Earth's magnetic field.
|
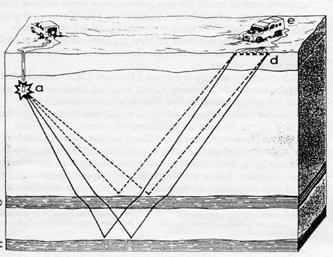
Seismic surveys test for various deposits, including oil, gas, and coal. Seismic surveying involves setting off explosions or vibrations that send shock waves down into the ground and timing their return from surfaces that bend or bounce them back. The speed of their return indicates the depth and nature of the rocks below.
|
All these prospecting methods merely hint at what lies underground. Only exploration can prove an ore is actually there and rich and big enough to be worth mining. If prospecting gives encouraging results, exploration follows. This means drilling sample cores or digging trial trenches to find out if development would pay.
(David Lambert “The Field Guide to Geology”, Cambridge University Press, 1998)
Дата добавления: 2015-09-10; просмотров: 91 | Поможем написать вашу работу | Нарушение авторских прав |